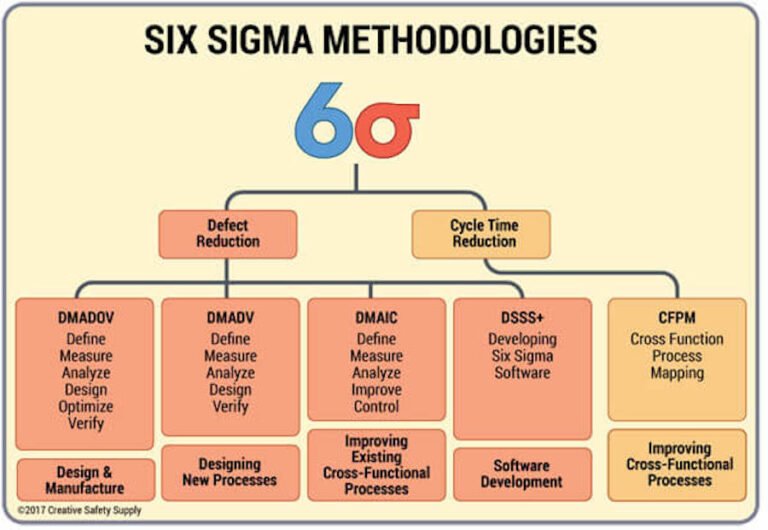
Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology that improves the quality of processes, products, and services by reducing defects and increasing efficiency. The approach aims to achieve a process capability of 3.4 defects per million opportunities or fewer.
The methodology consists of five phases: Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control (DMAIC).
- Define: The problem or opportunity is identified, and the project scope is defined.
- Measure: Data is collected and analyzed to determine the current performance of the process.
- Analyze: The root cause of the problem is identified, and potential solutions are generated.
- Improve: The best solution is selected, implemented, and its effectiveness is monitored.
- Control: The process is standardized and continuously monitored to ensure sustained improvement.
Six Sigma also has a design-focused approach called Design for Six Sigma (DFSS). This methodology is used to develop new processes, products, or services. The DFSS approach consists of six phases: Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, Verify, and Control (DMADVC).
Six Sigma is widely used in various manufacturing, healthcare, finance, and service industries. The methodology has successfully reduced defects, improved customer satisfaction, and increased profitability.
Six Sigma certification is available through various organizations and programs, including the American Society for Quality (ASQ) and the Six Sigma Academy. Six Sigma certified professionals, known as Black Belts, are trained to lead Six Sigma projects and mentor others in the methodology.
In conclusion, Six Sigma is a proven methodology for continuous improvement and quality assurance. Its focus on data-driven decision-making and structured approach to problem-solving have made it a popular choice for organizations seeking to improve their processes, products, and services.