What are Management Systems?
Basic Definitions
What are the objectives of a management system?
What should be included in a Food Safety Management System?
What are the Food Safety Critical Success factors?
What are the business benefits of a Food Safety Management System?
Definitions
Management System – system to establish policy and objectives and to achieve those objectives (ISO 9000)
Food Safety – concept that food will not cause harm to the consumer when it is prepared and / or eaten according to its intended use (ISO 22000, Section 3.1)
Food Safety Management System (FSMS) – a set of interrelated or interacting elements to establish policy, objectives and to achieve those objectives, used to direct and control an organization with regards to food safety (ISO/TS 22003:2007, Section 3.5)
Objective of Management System Implementation
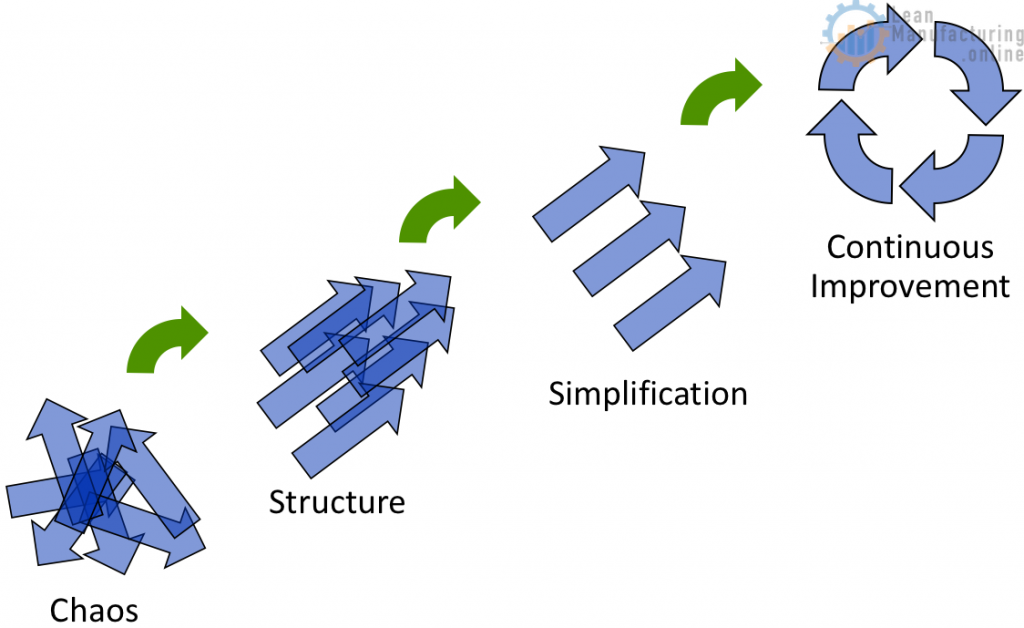
Food Safety Critical Success Factors
- Food Safety policy, objectives, and activities that reflect business objectives;
- Approach to food safety consistent with the types of organization;
- Visible support and commitment from all the levels in the organization;
- A good understanding of Food safety requirements, Hazard analysis and Risk management;
- Effective communication of food safety requirements to the staff and other interested parties;
- Effective implementation of prerequisite program;
- Adequate Financial Support;
- Appropriate Awareness, Training and Education;
- Effective emergency preparedness and accident management process.
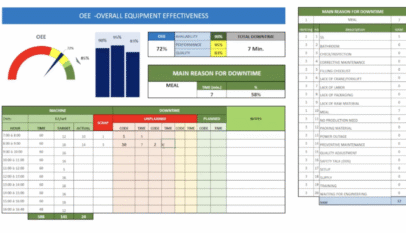
FSMS Continuous improvement & TPM
Agenda
- Usage of Deming PDCA continuous improvement cycle in factory applications
- PDCA & TPM
PDCA continuous improvement
Factories should be using the Deming continuous improvement cycle to continuously improve their Food Safety Systems
Factories should already be using the plan, do, check act continuous improvement cycle as a component of TPM. We should be applying our current continuous improvement activities towards FSSC 22000 implementation.
Plan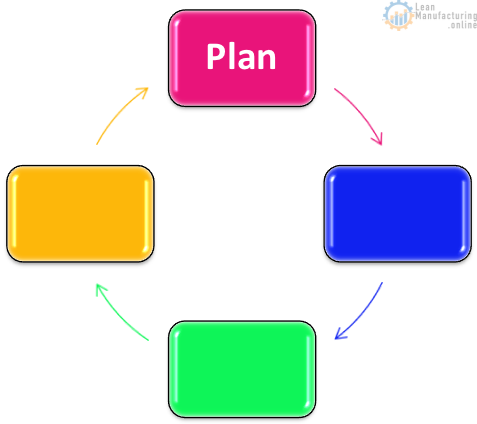
- Incident KPI’s
- CCPMU KPI’s
- Employee training
- Company standards
- HACCP peer reviews
- Design HACCP
Plan activities include setting KPI objectives, corporate standards, HACCP peer reviews, design HACCP and employee training.
Do
(Development and Implementation)
- Operational HACCP plans
- OPRP’s
- PRP’s
- SOP’s
Do activities include the development and implementation of factory food safety management systems.
Check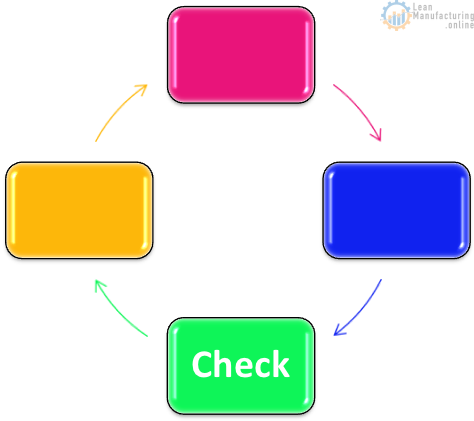
- Internal Audits
- QVP Self Assessment
- Foreign Material risk assessment
- Hygiene monitoring
- Annual HACCP Reassessment
- Operational Quality Reviews
- Allergen risk assessment
- Food safety team open actions
Act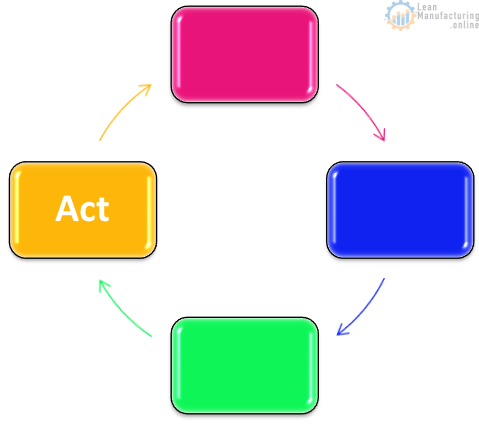
Improvement plan implementation
- Quality self assessments
- OQR’s
- Foreign material risk assessment
- Allergen risk assessment
- HACCP reassessment
- Food safety team open action completion
Focused Improvements
Autonomous Maintenance (Ability to sustain)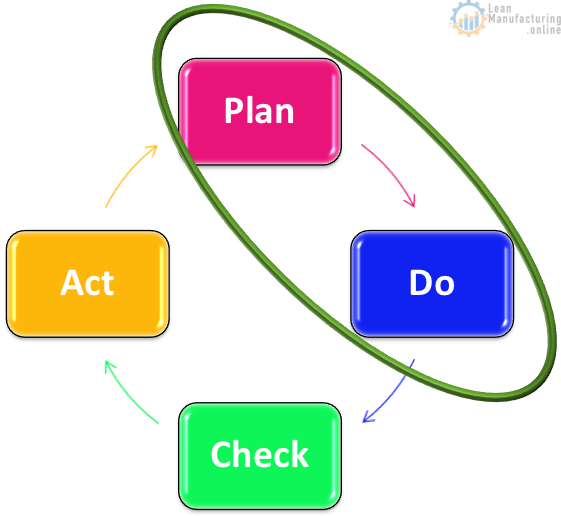
Examples:
- Procedures
- Cleaning
- Preventive Maintenance
- Inspection
- Standardization
FSMS Focused Improvement (Ability to improve)
Examples: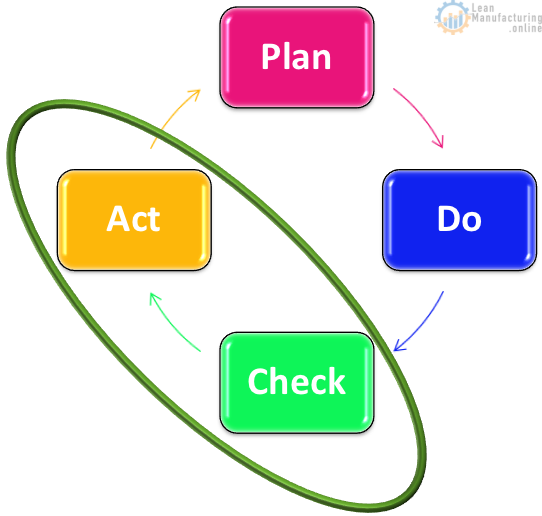
- Incident reduction
- CCPMU reduction
- Examples of tools:
- Loss tree
- Internal audits
- Why, why analysis
- Fishbone diagrams
- Control charts
- Pareto charts
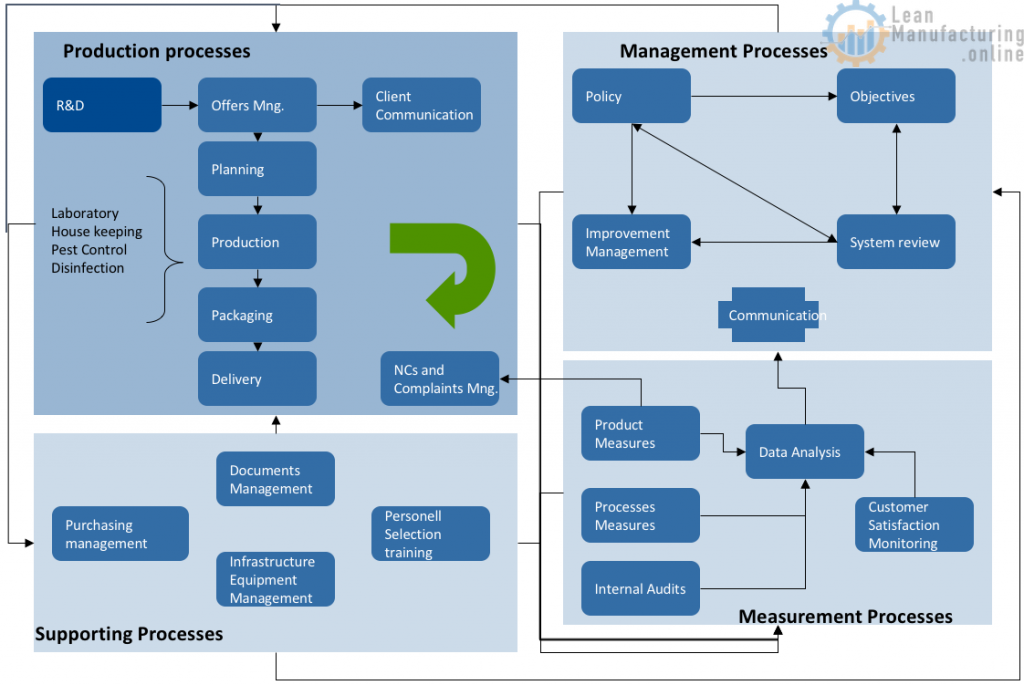
PDCA and Process Approach
PDCA How it works

PDCA applies to all Processes!!!
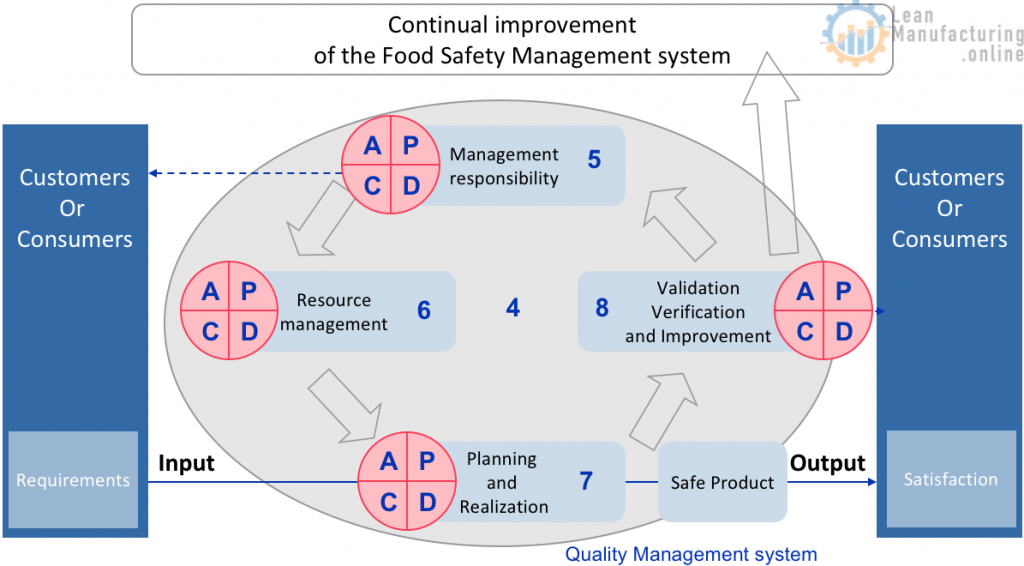
PDCA in ISO 22000
FSSC 22000 Food Safety Management System
- Explain the origin of the FSSC 22000 Scheme.
- Explain documents involved in the approved GFSI standard.
- Explain the interaction between ISO 22000, ISO/TS 22000-1 and FSSC Additional Documents (Part I).
Main purpose of a Food Safety Management System (FSMS)
- Ensure hazard control by combining the PRPs, Operational PRPs and the HACCP plan
- Useful tool for ensuring compliance with requirements (legal / customers)
- Continuous improvement of processes based on objective measurement
- Process approach – provides a method for risk management
ISO22000:2005

What is FSSC 22000?

- FSSC 22000 (Food Safety System Certification) is a combination of: ISO 22000:2005, ISO/TS 220002-1 ( previously PAS 220) and the Additional Requirements (Part I);
- Developed and owned by the Foundation for Food Safety Certification and supported by the Confederation of the Food and Drink Industries of the European Union (CIAA);
- FSSC = Foundation for Food Safety Certification;
- Currently approved only for specific sectors in the food chain.
A process based ISO 22000:2005

The Framework of ISO 22000:2005
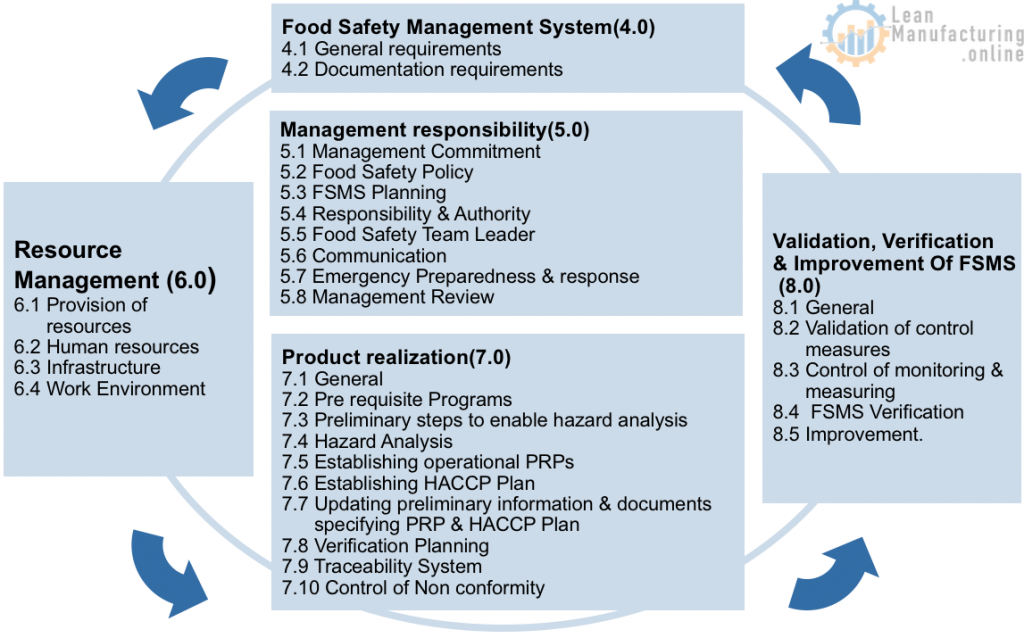
ISO 22000 Requirements
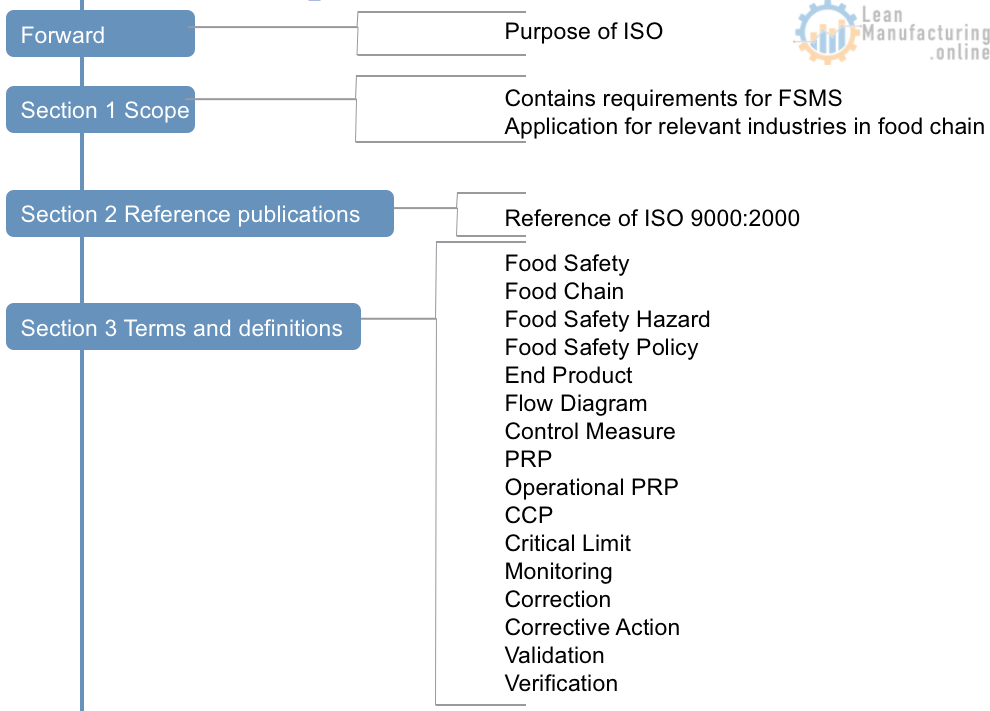

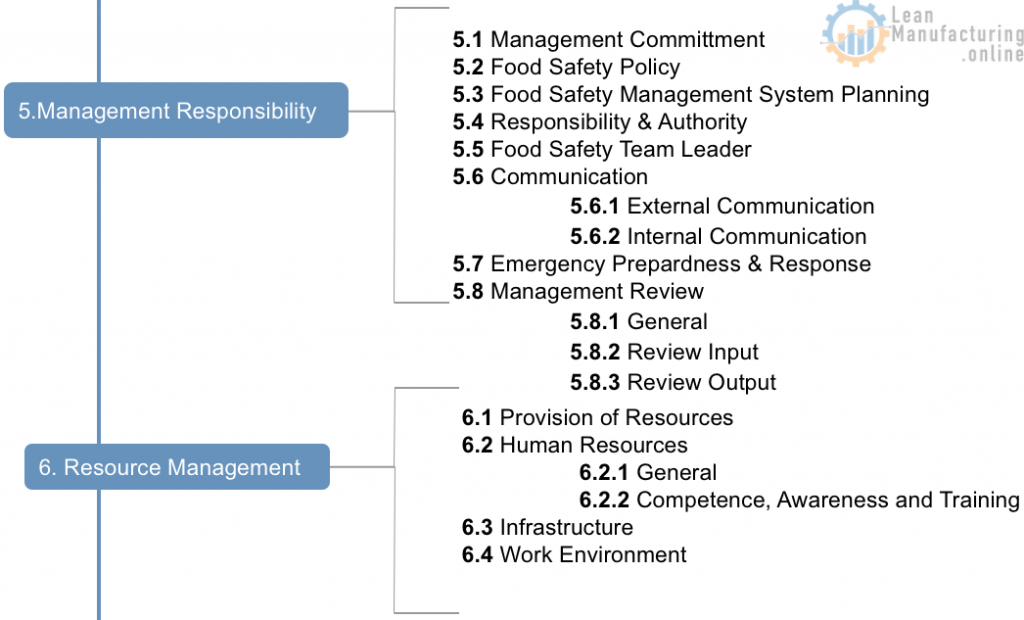

Most of the clauses in section 7 are covered by the development and implementation of the operational HACCP study.




















Great article, thank you for sharing. I liked that you added in all of the flow charts and organization charts. This helped give the article a better understanding to a reader that might not know a whole lot about Food Safety System Certification. Our headquarters are based in Adelaide, South Australia and we have hired JLB http://www.jlb.com.au/business/management-system/main/fssc-22000-and-iso-22000/ to implement our FSSC. Having this system in place has helped us a lot especially when it comes to future auditing.